

These bones tend to have more complex shapes, like the vertebrae that support the spinal cord and protect it from compressive forces. Irregular BonesĪn irregular bone is one that does not have any easily characterized shape and therefore does not fit any other classification. Flat bones serve as points of attachment for muscles and often protect internal organs. Examples include the cranial (skull) bones, the scapulae (shoulder blades), the sternum (breastbone), and the ribs. The term “ flat bone” is somewhat of a misnomer because, although a flat bone is typically thin, it is also often curved. Short bones provide stability and support as well as some limited motion. The only short bones in the human skeleton are in the carpals of the wrists and the tarsals of the ankles. Short BonesĪ short bone is one that is cube-like in shape, being approximately equal in length, width, and thickness. Long bones function as levers they move when muscles contract. Long bones are found in the arms (humerus, ulna, radius) and legs (femur, tibia, fibula), as well as in the fingers (metacarpals, phalanges) and toes (metatarsals, phalanges). Keep in mind, however, that the term describes the shape of a bone, not its size.
Long BonesĪ long bone is one that is cylindrical in shape, being longer than it is wide.

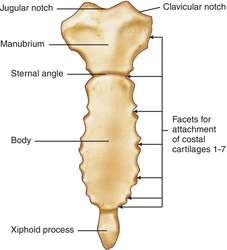
Figure 6.6 Classifications of Bones Bones are classified according to their shape.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
